Deputy Prime Minister-MOEF Minister Hong leads Korean delegation to 2019 Annual Meeting Board of Governors of the Asian Development Bank
_홍남기2.jpg)
Deputy Prime Minister and Minister Hong Nam-ki of the Ministry of Economy and Finance.(Photo:MOEF)
Deputy Prime Minister and Minister Hong Nam-ki of the Ministry of Economy and Finance (MOEF) will head a Korean delegation to the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Board of Governors of the Asian Development Bank (ADB), to be held from May 3 to May 5 in Fiji.
The delegates include the governor of the Bank of Korea and heads and representatives of commercial banks, including Shinhan Financial Group, Kookmin Financial Group, Hana Financial Group, NH Financial Group, Woori Bank, Korea Development Bank, IBK, and Korea Eximbank as well as representatives of other financial institutions and the financial industry, including Korea Asset Management Corp, Korea Deposit Insurance Corp, Korea Federation of Banks, Korea Financial Investment Association, and the Incheon Municipal goverment.
During the 2019 ADB annual meeting, the Korean delegation will promote Korea’s hosting the 53rd Annual Meeting of its Board of Governors, to be held at Songdo ConventiA in Incheon, from May 2 to May 5, 2020. This will be the third time the Republic of Korea will host the meeting.
It hosted ADB’s 37th Annual Meeting in Jeju Island in 2004 and ADB’s 3rd Annual Meeting in Seoul in 1970. Korea is a founding member of ADB. The Annual Meeting is the largest gathering of the bank and a unique opportunity for ADB Governors to engage in focused discussion on development issues and challenges facing Asia and the Pacific.
About 3,000 participants regularly join the meeting, including finance ministers, central bank governors, senior government officials, members of the private sector, representatives of international organizations and civil society organizations, youth, academia, and the media. ADB is committed to achieving a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Asia and the Pacific, while sustaining its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty. Established in 1966, it is owned by 67 members - 48 from the region.
Govt. to Work on Revisions to Project Feasibility Study; Works out a roadmap to a “hydrogen economy”
Deputy Prime Minister Hong presided over the 12th Ministerial Meeting on “Boosting the Economy,” the 11th ministerial meeting on the economy of this year, held on April 3.
The 12th meeting discussed revisions to the current project feasibility study, measures to promote the development of 5G services, “5G+ Measures,” and a roadmap to a hydrogen economy with regard to standardization. DPM Hong also talked about why the government has decided to propose supplementary budgets, explaining the areas the budget will focus on.
The following is a summary of DPM Hong’s keynote address.
The government decided on April 2 to propose a supplementary budget for 2019 to help reduce fine dust levels and shore up the economy amid weakening exports and falling employment rates among those in their 30s and 40s. The 2019 supplementary budget will be drafted with its focus on the following.
- Provide support for fine dust reduction, which will include early scrapping of old vehicles and purchases of high-tech equipment for measuring and analyzing fine dust affecting the country
- Shore up the economy: Increase export financing and strengthen support for ventures and tourism infrastructure
- Increase support for job creation and strengthen social safety nets
Revisions to project feasibility study
Korea adopted the current system of project feasibility study in 1999, which has since then successfully worked for the country’s fiscal resources to be used efficiently. However, it is time to revise the system in a way to better reflect changes in economic and social environments. The revision will reflect:
- Region specific conditions: Apply lower economic analysis standards to regions outside the Seoul Metropolitan Area
- Growing non-economic concerns, such as concerns for safe environment and security
- A need to adjust welfare projects when the original fails to pass the feasibility study
- A need to shorten the feasibility study and involve various point of views: Shorten the feasibility study from an average of 19 months to less than one year, and include Korea Institute of Public Finance in feasibility assessment, in addition to KDI (Korea Development Institute) and KISTEP (Korea Institute of Science & Technology Evaluation and Planning)
5G+ Measures
The government has drafted measures to promote the development of 5G services, the so-called 5G+ Measures, which focuses on the birth of new industries and job creation, including suppliers.
The measures also reflect the country’s pursuit of innovation-driven growth. The government will continue to work on the final version of the measures. Roadmap to a hydrogen economy.
The government has prepared a roadmap to a hydrogen economy, focusing on standardization, which contains the following. - Support the development of global standard technologies, and work for a total of 15 technologies to be proposed for global standards by 2030
- Develop 30 Koreas Standards (KS) technologies by 2030
- Grow standardization experts and support standardization efforts by the private sector.
Govt. to Proceed with Semiconductor Cluster Development
Prime Minister Hong presided over the 11th Ministerial Meeting on Boosting the Economy on March 27. The 11th meeting discussed steps to be taken towards the development of a semiconductor cluster in the Seoul metropolitan area and the outcomes of the government’s deregulation efforts.
DPM Hong talked about the current economic situation. The following is a summary of DPM Hong’s keynote address.
The March consumer sentiment index has just been released, showing improvement for a fourth consecutive month. This is not good news when the country’s exports have been weakening and concerns over a global economic slowdown are increasing. The government will work hard for this to lead to real economic improvement.
The government has decided to develop a large-scale semiconductor cluster in Yongin, a city located in the Seoul metropolitan area. The development project is expected to attract around 120 trillion won worth of private sector investment over the next 10 years, creating around 17,000 jobs and added value of about 188 trillion won.
When completed, a total of four main semiconductor manufacturing facilities will be located in a site as large as about 4.46 million square meters, along with over 50 suppliers. The government will work on regulatory procedures, such as eminent domain and development permit, and work for the construction to begin in 2021. Outcomes of government’s deregulation efforts
The MOEF has looked into whether or not existing regulations are necessary since Jan. 23, when the government adopted a new regulatory system in which government officials are obliged to prove that a certain regulation should exist.
The Ministry began with regulations on FX transactions, national contracts and public procurement, and of a total of 272 regulations, 83 have been lifted or improved. The government will continue with these deregulation efforts, other ministries joining in improving their regulations.
Current Economy Situation
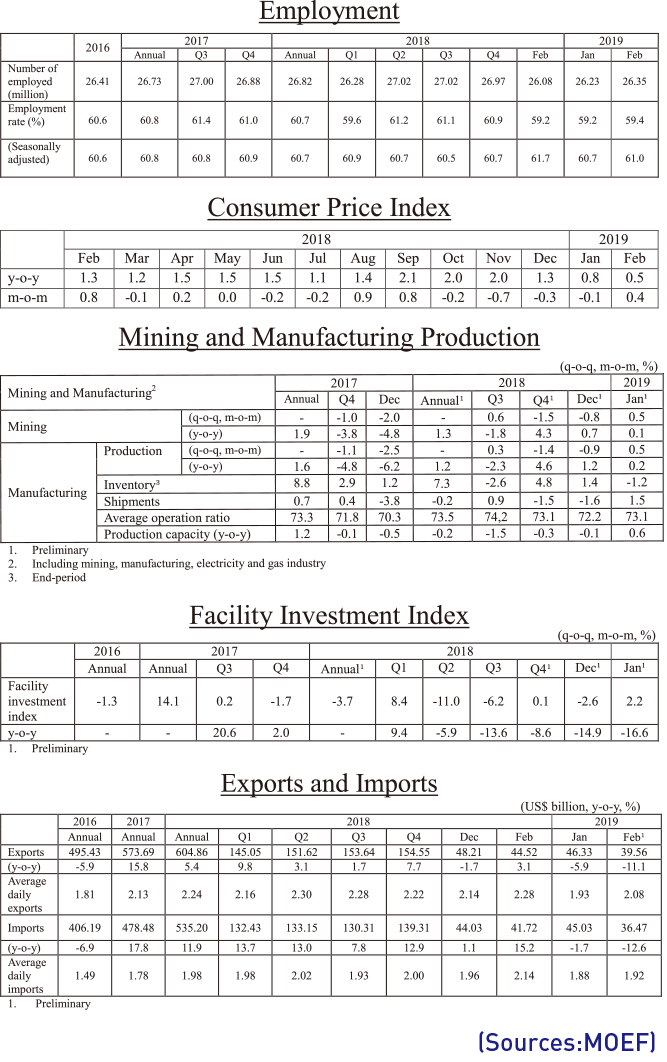
The economy has been improving in 2019 as industrial activities rose in January and economic confidence continued to rise in February. Jobs grew significantly in February compared with the previous month, and consumer prices remained stable.
Industrial production rose in January by 0.8 percent month-on-month due to strong mining and manufacturing (up 1.2% month-on-month), service output (up 0.9%, m-o-m) and construction completed (up 2.1% month-on-month).
Consumption and investment improved in January: Retail sales rose as well as facility investment and construction completed.
Exports remained weak in February, falling 11.1 percent year-on-year due to weak semiconductors and slowing down global economies, including the Chinese economy.
The consumer sentiment index rose for the third consecutive month in February, up 2 points to 99.5, and the business sentiment index improved 2 points to 69. The BSI outlook for March jumped 11 points to 76.
The cyclical indicator of the coincident composite index fell in January, as well as the cyclical indicator of the leading composite index, by 0.1points and 0.4points, respectively, compared to a month ago.
The economy added 263,000 jobs in February as service jobs increased and also due to the government’s job creation programs. The unemployment rate went up by 0.1 percentage points due to increased job seekers. Consumer prices in February rose 0.5 percent compared to a year ago, fresh food prices being stable and oil prices continuing to fall.
In February, KOSPI declined and the won weakened. Treasury bond yields fluctuated. Housing prices continued to decline in February (down 0.15% month-on-month) and Jeonse (lump-sum deposits with no monthly payments) prices continued to fall (down 0.22% month-on-month).
There has been a positive momentum into this year backed by improving industrial activities However, uncertainties linger amid concerns over global economic slowdown, weak semiconductor markets, US-China trade relationship and Brexit. The government will strengthen its risk management, and will try to find ways to boost the economy and promote inclusiveness.
The government will work to successfully implement measures to encourage exporters and ventures, as well as plans to support industrial innovation.
Financial Regulatory Sandbox Launched
The Financial Services Commission (FSC) has officially launched a “financial regulatory sandbox” as the Special Act on Financial Innovation Support takes effect on April 1.
Since the preliminary application period for financial regulatory sandbox was open last January, the FSC received 105 applications. Among them, 19 applications were shortlisted for priority review by an evaluation committee, composed of government officials and private experts. The evaluation committee held its first meeting today to discuss how to run the regulatory sandbox scheme.
2018 Govt. Financial Statement
The consolidated fiscal account posted a surplus of 31.2 trillion won, an increase of 7.1 trillion won (0.4 percent points to GDP) compared with the previous year. Excluding social security funds (1), the fiscal account registered a deficit of 10.6 trillion won, deficits falling 7.9 trillion won (0.5 percentage points to GDP) compared with the previous year.
The consolidated fiscal account improved for the third consecutive year in 2018 backed by increased corporate earnings and strong asset markets.
The central government debt was 651.8 trillion won in 2018 (36.6 percent to GDP), an increase of 24.4 trillion won compared with 2017 (627.4 trillion won, or 36.3 percent to GDP). Debt grew at the slowest pace since 2009. Net national assets were 441.0 trillion won, national assets worth 2,123.7 trillion won and national liabilities worth 1,682.7 trillion won.
